Closing the Skills Gap: Vocational Training Evolution by 2026

U.S. vocational training programs are rapidly transforming by 2026, embracing technology and industry partnerships to effectively close the national skills gap and prepare a competent workforce for evolving demands.
The U.S. economy currently faces a significant challenge: a persistent shortage of skilled workers in various critical sectors. This phenomenon, often referred to as the skills gap, threatens innovation and economic growth. By 2026, the landscape of U.S. vocational training programs is undergoing a profound transformation, actively working towards closing the skills gap through innovative approaches and strategic adaptations.
Understanding the Evolving Skills Gap in 2026
The skills gap in the United States is not a static problem; it is a dynamic challenge continually shaped by technological advancements, global market shifts, and changing industry demands. By 2026, this gap has become more pronounced in certain areas, driven by the rapid adoption of automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Industries such as advanced manufacturing, cybersecurity, renewable energy, and healthcare technology are experiencing an acute shortage of qualified professionals. Traditional educational pathways often struggle to keep pace with these swift changes, leaving many job seekers unprepared for the roles employers desperately need to fill.
Key Drivers of the 2026 Skills Gap
Several factors contribute to the current skills deficit, making it a complex issue requiring multifaceted solutions. Understanding these drivers is crucial for designing effective vocational training programs.
- Technological Disruption: Automation and AI are redefining job roles, demanding new digital and analytical proficiencies.
- Aging Workforce: A significant portion of the skilled workforce is nearing retirement, taking valuable institutional knowledge with them.
- Misalignment in Education: Traditional curricula often do not adequately prepare students for the specific technical and soft skills required by modern industries.
- Perception of Vocational Careers: A lingering stigma sometimes discourages individuals from pursuing skilled trades, despite high demand and good pay.
Addressing these drivers requires a concerted effort from educators, industry leaders, and policymakers to align training with real-world needs. The evolution of vocational training is directly responding to these pressures, aiming to create a more agile and responsive educational ecosystem.
Adaptive Curricula: Tailoring Education to Industry Needs
One of the most significant transformations in U.S. vocational training programs by 2026 is the shift towards highly adaptive and industry-specific curricula. No longer are programs designed in isolation; instead, they are co-created with input from leading businesses and industry consortia.
This collaborative approach ensures that the skills taught are directly relevant to current and future job requirements. It moves beyond theoretical knowledge, emphasizing practical, hands-on competencies that make graduates immediately employable and productive.
Industry Partnerships and Program Design
Vocational institutions are forging stronger ties with local and national industries. These partnerships are instrumental in shaping curriculum development, providing insights into emerging technologies, and identifying critical skill shortages. Companies are investing in these programs, offering equipment, guest lecturers, and even apprenticeship opportunities.
- Advisory Boards: Industry professionals serve on advisory boards, guiding curriculum updates and ensuring relevance.
- Real-World Projects: Students engage in projects directly sourced from industry partners, gaining practical experience.
- Equipment Donations: Companies often donate cutting-edge machinery and software, allowing students to train on current tools.
This symbiotic relationship benefits both sides: businesses gain a pipeline of skilled talent, and students receive an education that is highly valued in the job market. The focus is on creating a seamless transition from classroom to career, minimizing the need for extensive on-the-job training.
The adaptability of these curricula also extends to their modular nature. Many programs are now designed with stackable credentials, allowing students to earn certifications and degrees incrementally, responding to immediate job market demands while also providing pathways for continuous learning and career advancement.
Integrating Advanced Technology and Digital Skills
By 2026, the integration of advanced technology and digital literacy has become a cornerstone of U.S. vocational training. This goes beyond simply teaching how to use software; it involves embedding digital fluency into every aspect of technical education. From augmented reality (AR) for equipment maintenance to data analytics for process optimization, technology is enhancing how skills are taught and practiced.
Vocational programs are investing heavily in state-of-the-art labs and simulation environments that mirror real-world industrial settings. This allows students to gain experience with complex machinery and systems in a safe, controlled, and cost-effective manner. The goal is to produce graduates who are not just skilled technicians, but also digitally competent problem-solvers.
Virtual and Augmented Reality in Training
Immersive technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are revolutionizing vocational education. These tools provide realistic training scenarios that would be impractical or dangerous in a traditional classroom setting. Students can practice intricate procedures, troubleshoot complex systems, and even collaborate remotely on projects.
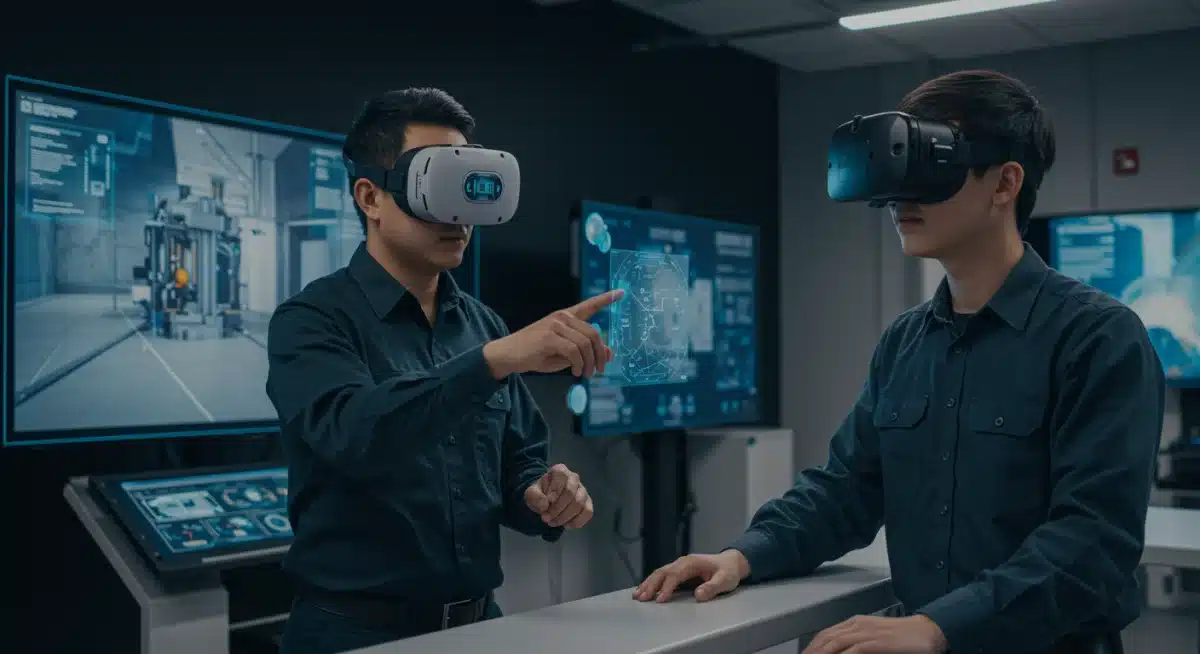


- Safe Practice: VR allows students to repeatedly practice high-risk tasks without actual danger or material waste.
- Enhanced Understanding: AR overlays digital information onto physical objects, aiding in assembly, repair, and diagnostics.
- Remote Learning: These technologies enable effective remote training, expanding access to specialized programs.
The widespread adoption of these technologies ensures that vocational graduates are not only familiar with industry-standard tools but are also adept at learning and adapting to new technological paradigms, a crucial skill in the rapidly evolving job market of 2026.
Flexible Pathways: Micro-credentials and Apprenticeships
The traditional model of a multi-year degree is being supplemented, and in some cases replaced, by more flexible and agile learning pathways. By 2026, micro-credentials and modern apprenticeships have emerged as powerful tools for rapid skill acquisition and career advancement, directly contributing to closing the skills gap.
Micro-credentials, often short-term certifications focused on specific competencies, allow individuals to quickly gain in-demand skills without committing to a full degree program. These can be stacked over time to build comprehensive skill sets or to upgrade existing qualifications.
The Rise of Modern Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships are experiencing a renaissance, evolving beyond traditional trades to encompass high-tech fields like IT, cybersecurity, and advanced manufacturing. These programs combine paid on-the-job training with related technical instruction, providing a direct route to employment and skill mastery.
- Earn While You Learn: Apprentices receive wages, making education accessible to a wider demographic.
- Guaranteed Employment: Successful apprentices often transition directly into full-time roles with their sponsoring companies.
- Industry-Recognized Credentials: Programs typically lead to certifications valued by employers nationwide.
This blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application ensures that apprentices are not only skilled but also deeply integrated into the company culture and specific operational needs. The flexibility offered by micro-credentials and apprenticeships caters to diverse learners, including recent high school graduates, career changers, and incumbent workers seeking to upskill.
Addressing Soft Skills and Employability
While technical proficiency remains paramount, U.S. vocational training programs in 2026 are placing increased emphasis on developing essential soft skills. Employers consistently report that critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, teamwork, and adaptability are just as crucial as technical expertise for workplace success.
These interpersonal and cognitive skills are no longer considered secondary; they are actively integrated into the curriculum through project-based learning, collaborative assignments, and simulated workplace environments. The goal is to produce well-rounded professionals who can navigate complex work dynamics and contribute effectively to team goals.
Cultivating a Holistic Skill Set
Vocational programs are moving towards a holistic development model, recognizing that a technically brilliant individual may still struggle without strong communication or critical thinking. They embed these skills into practical exercises and feedback mechanisms.
- Project-Based Learning: Encourages teamwork, problem-solving, and communication in simulated real-world scenarios.
- Communication Workshops: Focus on effective written and verbal communication relevant to specific industries.
- Critical Thinking Exercises: Develop analytical abilities to diagnose issues and propose innovative solutions.
By fostering these soft skills alongside technical competencies, vocational training graduates are better equipped to adapt to evolving job roles, collaborate effectively with diverse teams, and demonstrate leadership potential. This comprehensive approach significantly enhances their long-term employability and career trajectory, further contributing to closing the skills gap.
Funding and Policy Initiatives Supporting Vocational Growth
The evolution of U.S. vocational training programs by 2026 is significantly bolstered by renewed governmental and private sector funding, alongside supportive policy initiatives. Recognizing the critical role of skilled trades in economic stability and growth, there has been a concerted effort to invest in these educational pathways.
Federal and state governments are allocating substantial funds for program development, equipment upgrades, and student scholarships. This financial support helps institutions innovate, expand their offerings, and make vocational education more accessible and affordable for a broader range of students.
Government and Private Sector Collaboration
Policy initiatives are focusing on streamlining the accreditation process for vocational programs, encouraging public-private partnerships, and providing incentives for employers to participate in apprenticeship programs. The aim is to create a robust ecosystem that supports continuous skill development.
- Perkins V Act: Continues to provide federal funding for career and technical education programs.
- State-Level Grants: Many states offer grants specifically for vocational program expansion and student aid.
- Tax Incentives: Businesses receive tax breaks for investing in training infrastructure and apprenticeship programs.
These funding and policy initiatives are crucial for sustaining the momentum of vocational training reform. They ensure that institutions have the resources to adapt to new technologies and industry demands, while also making these vital career paths more attractive and viable for prospective students. The collective impact of these efforts is instrumental in effectively closing the skills gap across various sectors.
The Future Outlook for Skilled Trades in 2026 and Beyond
As we look beyond 2026, the future of skilled trades in the U.S. appears robust and increasingly sophisticated. The ongoing transformation of vocational training programs is not just a temporary fix but a fundamental reorientation of how the nation prepares its workforce. The emphasis on adaptability, technology integration, and strong industry ties ensures that vocational education remains at the forefront of economic development.
The perception of vocational careers is also shifting, with a growing recognition of the value, earning potential, and innovation inherent in skilled trades. This positive change, coupled with accessible and high-quality training, is attracting a new generation of learners who are keen to pursue hands-on, impactful careers.
The continuous dialogue between educators and industry will be vital. As new technologies emerge and existing ones evolve, vocational programs must remain agile, constantly updating their curricula and methodologies. The ability to anticipate future skill demands and proactively develop training solutions will be key to maintaining a competitive edge in the global economy.
Ultimately, the successful evolution of U.S. vocational training programs by 2026 is critical for national prosperity. By effectively closing the skills gap, these programs are empowering individuals with valuable careers and providing industries with the talent they need to innovate and thrive in an ever-changing world.
| Key Aspect | Impact on Skills Gap |
|---|---|
| Adaptive Curricula | Ensures training directly matches current and future industry demands. |
| Technology Integration | Prepares workers with digital fluency and experience in advanced tools. |
| Flexible Pathways | Offers quick skill acquisition through micro-credentials and apprenticeships. |
| Soft Skill Development | Enhances employability with critical thinking, communication, and teamwork. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Vocational Training in 2026
The main goal is to effectively close the U.S. skills gap by equipping the workforce with relevant, in-demand technical and soft skills, ensuring graduates are prepared for the evolving demands of industries like advanced manufacturing and IT.
Curricula are now co-created with industry partners, integrating real-world projects and insights from company advisory boards. This ensures that training is highly relevant and provides students with practical, hands-on experience directly applicable to job roles.
Technology, including VR and AR, is deeply integrated into vocational training. It provides immersive simulation environments for safe practice, enhances understanding of complex systems, and ensures students are proficient with cutting-edge tools and digital processes.
Yes, modern apprenticeships are highly relevant and growing. They combine paid on-the-job training with technical instruction in fields beyond traditional trades, offering direct employment pathways and valuable industry-recognized credentials for diverse learners.
Employers increasingly value soft skills like critical thinking, communication, and teamwork. Vocational programs integrate these through project-based learning, ensuring graduates are well-rounded professionals who can adapt, collaborate, and succeed in complex work environments.
Conclusion
The proactive evolution of U.S. vocational training programs by 2026 represents a critical national effort to bridge the persistent skills gap. Through dynamic curricula shaped by industry collaboration, the strategic integration of advanced technologies like VR, and the expansion of flexible learning pathways such as micro-credentials and modern apprenticeships, these programs are creating a highly competent and adaptable workforce. This comprehensive approach, coupled with a renewed focus on essential soft skills and robust funding initiatives, ensures that vocational education is not only responsive to current industry demands but also poised to meet the challenges and opportunities of the future, fostering both individual career success and broader economic prosperity.